linker是Android系统动态库so的加载器和链接器,也是Android脱壳一重要脱壳点,这里介绍一下此部分的Android源码,并介绍几个脱壳点,及分析过程中产生的反调试手段,学习Linker的加载和启动原理,又需要介绍so的加载和启动。
系统 :Android4.4-r1
linker源码的位置 : Android/bionic/linker
0x00 加载与启动so
1、Java层中声明加载某个so文件以共享,则可在Java层声明代码:
1 | static{ |
其对应的执行流程如下:
1、 定位到文件Dalvik/vm/native/java_lang_Runtime.cpp
2、 调用Dalvik_java_lang_Runtime_nativeLoad -> Dalvik/vm/Native.cpp:dvmLoadNativeCode
具体代码如下,我略过一些错误判断代码,这段代码以/ 说明 /的形式省略
1 | bool dvmLoadNativeCode(const char* pathName, Object* classLoader, |
从上面的代码我们可看出
1、Android系统加载so文件时使用了dlopen函数;
2、定位JNI_OnLoad()方法,则dlsym(handle, “JNI_OnLoad”);
3、执行JNI_OnLoad()方法:(*func)(gDvmJni.jniVm, NULL)
我们查找加载so文件的函数dlopen在bionic/linker/dlfcn.c中,而此函数有主要调用了do_dlopen函数,这里对dlopen函数不详细赘述,主要解析一下do_dlopen函数,而此关键函数正是在Linker中。接下来详细分析Linker源码。
0x01 Linker源码总览
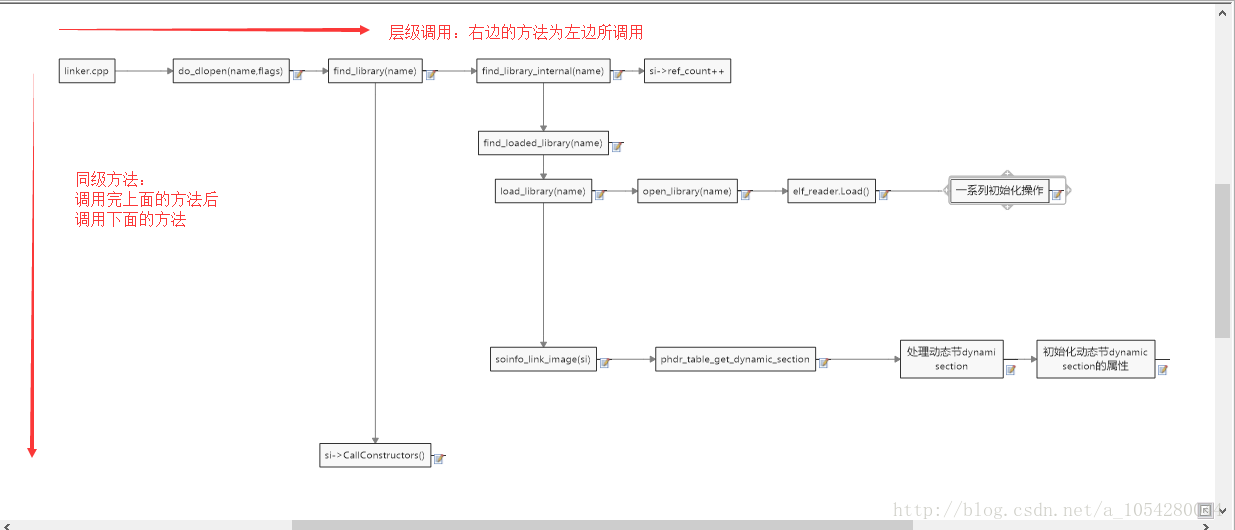
0x02 do_dlopen
先贴上代码:
1 | soinfo* si = find_library(name);//**完成so的加载到内存的工作 |
嗯,注释简单明了,接下来解析find_library(name)与si->CallConstructors()。
0x03 续0 find_library
作用:完成so的加载到内存的工作,成为是否加载过该so的重要依据
1 | static soinfo* find_library(const char* name) {//成为是否加载过该so的重要依据 |
嗯,还是很清晰,里面的调用的方法先放下先,我们现分析如下方法。
0x04 si->CallConstructors()
完成so及本身的构造函数的调用。完成so文件的加载
1 | /***省略一大堆代码,下面是主要函数****/ |
这主要是完成so文件的加载,然后遍历所有动态节,再根据标签d_tag ==DT_NEEDED调用依赖库的构造函数,再调用自己的一系列构造函数,以及init_arry函数,其中后面两个函数分别是so文件和dex文件的脱壳点,这样就结束了so文件的加载,但分析远远没有结束,我们需要回过头来解析find_library方法。
0x05 find_library 之find_library_internal()
操作:寻找相应的so信息
1 | static soinfo* find_library_internal(const char* name) { |
注释很明白,整理一下基本流程:
1、find_loaded_library():寻找相应的so信息
2、load_library():真正加载so文件的函数
3、soinfo_link_image():处理动态节dynamic section,初始化动态节dynamic section的属性
0x06 find_library_internal() 之 find_loaded_library()
1 | //寻找相应的so信息 |
0x07 find_library_internal() 之load_library()
操作:真正加载so文件的函数
1 | static soinfo* load_library(const char* name) { |
这里着重强调一下elf_reader.Load()方法:
1 | bool ElfReader::Load() { |
可以看出读取elf的操作,源码中看出只读取了Program 段,这也是很多加固进行抹头操作的原因:IDA只通过加载section Header段,来读取so文件,而实际上源码只读取了Program段,如果只是将section Header段抹头了,IDA便无法正常解析so文件,而Android系统却可以正常解析so文件,这也是一种反调试手段。
再后来就进行一系列对so文件的初始化操作:
1 | si->base = elf_reader.load_start(); |
其中si结构体如下(可略):
1 | struct soinfo { |
0x08 find_library_internal() 之soinfo_link_image(si)
在si = load_library(name)获得了so文件的info之后,就开始进行一系列操作:
1、定位动态节;
2、解析动态节;
3、加载动态节
4、重定位
1、定位动态节:
1 | phdr_table_get_dynamic_section(const Elf32_Phdr* phdr_table, |
值得注意的是,这里源码加载动态节的时候只加载了第一个动态节,后面的动态节都没有加载,因此我们可以自己自定义多个programm段中的动态节区,然后在section header中也改变相应的数据,这样IDA解析的信息是有所偏差的,因为Android系统实际上只读取了第一个动态节。
2、解析动态节。
解析代码如下:
1 | for (Elf32_Dyn* d = si->dynamic; d->d_tag != DT_NULL; ++d) { |
3、加载依赖库
1 | //********加载依赖库 (NEEDED) Shared library: [liblog.so] |
4、重定位操作
1 | if (si->has_text_relocations) {//重定位操作 |
其中具体的意义参见以下博客
http://blog.csdn.net/feibabeibei_beibei/article/details/53004525
0xFF 收尾
1、dlopen执行完毕后
2、调用 vonLoad = dlsym(handle, “JNI_OnLoad”)定位JNI_Onload
3、再执行version = (*func)(gDvmJni.jniVm, NULL);执行JNI_Onload
期间可以有三个断点:
.init->.init_array->JNI_Onload->java_com_XX.
反调试思路:
1、section Header的抹头操作
2、自定义多个动态节
这里留个坑,就是未进行对全局变量gDvm的解析,师傅们多多指教哇~
参考链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/feibabeibei_beibei/article/details/53004525
https://xianzhi.aliyun.com/forum/read/316.html
http://blog.csdn.net/maspchen/article/details/50568693